As a Result of a Cyberattack, Ads for Illegal Chinese Casinos Ended Up on 150K Websites
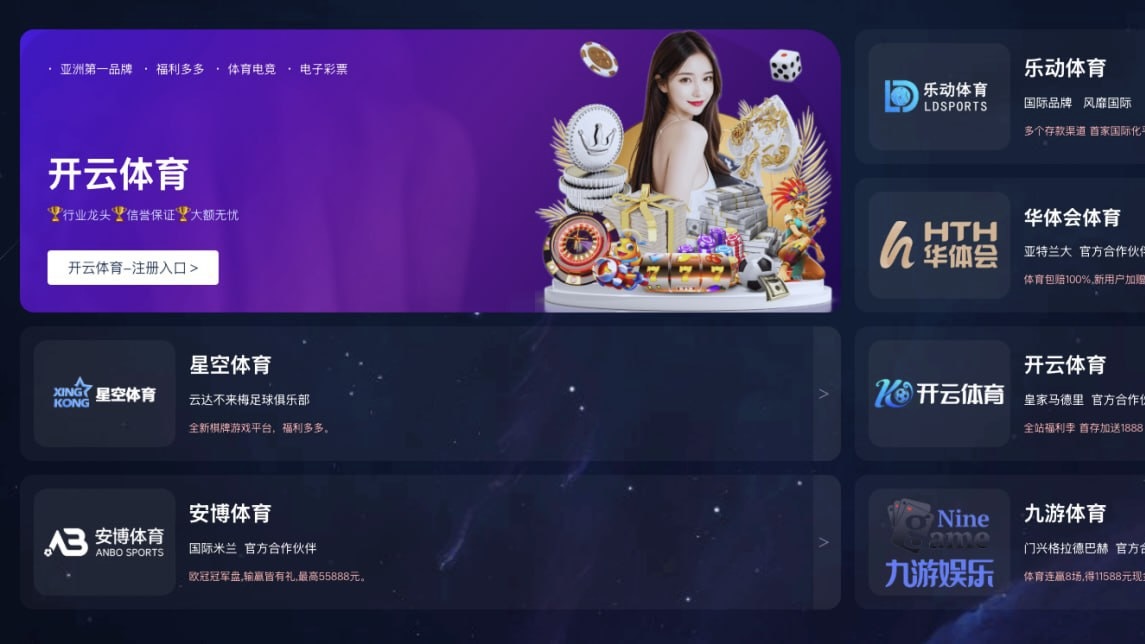
In February 2025, a large-scale cyberattack was uncovered, affecting over 150,000 websites worldwide. Hackers used malicious scripts that injected fake interface elements into pages, redirecting visitors to illegal Chinese casinos. Let’s take a closer look at how this attack works, its scale, and protection methods.
Characteristics of the Attack
The attack, discovered by the c/side research team, involved injecting malicious scripts that created the illusion of website legitimacy. Hackers used hidden interface elements with a fake fullscreen interface to redirect users to gambling sites targeting the Chinese audience.
Use of <iframe> and HTML Encoding
To hide the true purpose of the attack, the attackers used the <iframe> element, which was injected into the pages, replacing their content. This method allowed them to create the appearance of a regular website while visitors were actually redirected to offshore gambling platforms.
To complicate detection, the attackers’ code was encrypted using HTML Entity encoding. This concealed the actual script address and made it more difficult to detect through standard analysis methods.
Stages of the Attack
- Script Injection
Attackers add scripts to website pages that load alongside regular content. These scripts create a fullscreen window, which then redirects the user to gambling pages. - Code Obfuscation
The malicious scripts use obfuscation (concealment) techniques to complicate analysis. For example, JavaScript methods and elements such aseval()andsetInterval()mask the real actions of the script, making it difficult to detect. - Fake Branding
To increase trust, hackers used logos and design elements of well-known brands like Bet365 and other casinos. This helped create the illusion that users were visiting legitimate sites. - Multi-stage Redirects
Once the user reached a fake page, they were redirected to other sites that could block access from different regions. This was done to primarily target Chinese-speaking users, as well as users from the USA and Hong Kong.
Protection Methods Against Such Attacks
To protect against such attacks, website owners should regularly check their code for suspicious scripts and injections. Here are some key steps for protection:
- Check for <iframe> Injection
It is important to monitor any changes in the code, especially for the appearance of hidden <iframe> elements that may have been injected into the site. - Use Code Analysis Tools
To detect obfuscated scripts, online tools such as CyberChef can be used to decode HTML entities and analyze JavaScript code. - Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular checks and security audits on your website to identify suspicious code changes promptly. - Update CMS and Plugins
Updating the content management system (CMS) and plugins helps reduce vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit to infiltrate the site.
Scale of the Attack
At the time of analysis, more than 150,000 infected websites were recorded, and this number continues to rise. Hackers are actively using new obfuscation techniques and modifying the behavior of the attacks, making them increasingly difficult to detect and prevent.
Additionally, thanks to open code analysis tools such as PublicWWW, researchers were able to identify all infected websites. This data allows website owners to respond to the threat quickly.
Conclusion
The large-scale attack, affecting more than 150,000 websites, is a vivid example of how modern threats are becoming increasingly complex and sophisticated. It is crucial for website owners to stay alert and conduct regular security audits to minimize risks for their users.
